THIS POST IS ABOUT THE VARIOUS SOURCES WHERE YOU CAN LOOK FOR BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING PROJECTS ONE OF THE MOST POPULAR OUT OF THEM IS THE WEBSITE OF UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN RELATED TO BIOMEDICAL DESIGN PROJECTS THERE
SO IF YOU HAVE A TROUBLE IN CHOOSING PROJECTS FOR YOU DO VISIT THIS SITE
BME DESIGN PROJECTS 2011
Scientists have been searching for a cure for diabetes for long, and now they have indications that it may be lurking somewhere in the stomach. Doctors have found that several diabetics who underwent bariatric surgery (stomach reduction) to treat obesity, have shown reduction in blood sugar levels. Now, they are studying the unforeseen positive impact of the surgery to see if a drug could be developed to mimic the effect of a reduced stomach. Quoting studies from Sweden, US and UK, London-based Dr Torsten Olbers, senior consultant, Imperial College, London said diabetics had been cured in many patients over a period of time and in several others there was a substantial improvement in the quality of life. “There have been cases of diabetics (type-2) not needing insulin after a bariatric surgery. Some may take time, while several others need to take only lower doses of insulin after ,” said Dr Olbers who is on a visit to the city. Dr Olbers will be speaking on the effects of bariatric surgery at a workshop organised by Apollo Hospitals on Saturday. Type-2 diabetes, a lifestyle disorder, is usually triggered by obesity and it becomes difficult to maintain sugar levels even with insulin if patients do not lose weight. As a last resort for weight management, one of the three most common bariatric procedures band, bypass or sleeve is performed where the volume of the stomach is reduced intake by at least 80%. Delhi-based diabetologist Dr Anoop Misra says the observation makes sense. “Bariatric surgery results in reduction of agents in the stomach that stimulates appetite. Moreover, it increases some other secretions of the intestine that aid better absorption of insulin,” he says. Dr Prasanna Kumar Reddy of Apollo Hospitals cites the case of his patient M Gowtham. Weighing 163kg, Gowtham had diabetes and hypertension before he underwent a bariatric surgery. “Not only that his weight has come down to 93 kg, his blood sugar has also stabilised without insulin injections,” said Dr Reddy. “I feel like a normal human being now. I do everything I have been just wanting to do for the past 20 years,” said Gowtham. Having seen several such cases, Dr Abeezar Sarla, senior lecturer in surgery at the University of Leeds, said bariatric surgeons should be called metabolic surgeons. Considering the increasing population of people with both obesity and diabetes, it would soon be a common surgery. However, surgeons warn that patients should be chosen carefully for the surgery. “It’s not a surgery for people with normal weight. And there are risks associated with it. At least one in 20 patients can develop complications like bleeding and leakage. It could cause death in one in 500 patients, a risk comparable to any other surgery. And in some people there is even resurgence of obesity,” said Dr Olbers. Read morehttp://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chennai/Weight-reduction-surgery-may-hold-key-to-diabetes-cure/articleshow/6307648.cms#ixzz0weGYbmtm
Permanent link to this post (472 words, estimated 1:53 mins reading time)
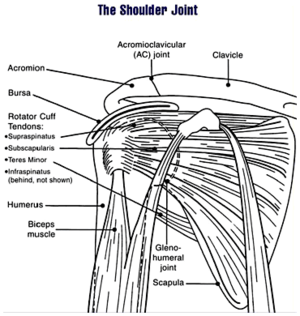
Image via Wikipedia
Joint replacement involves surgery to replace the ends of bones in a damaged joint. This surgery creates new joint surfaces.
In shoulder replacement surgery, doctors replace the ends of the damaged upper arm bone (humerus) and usually the shoulder bone (scapula) or cap them with artificial surfaces lined with plastic or metal and plastic. Shoulder joint components may be held in place with cement, or they may be made with material that allows new bone to grow into the joint component over time to hold it in place without cement.


